Generative artificial intelligence (genAI)—a branch of AI using algorithms to create new videos, images, and text that mimics its reference data—is revolutionizing yet another industry. Already leveraged by finance, consulting, and even law professionals, tech mammoths are set on integrating genAI into healthcare.
Unlike other forms of AI already used within healthcare, genAI can create predictive models to determine diagnoses and treatments based on existing patient data. While traditional AI focuses on detecting patterns, making decisions, gathering analytics, and classifying data, genAI produces new content (e.g., chat responses, designs, etc.) and synthetic data.
From streamlining medical processes like scribing prescriptions to responding to patient messages, the list of potential AI use cases is endless. But that hasn’t stopped experts from scrutinizing where genAI’s shortcomings could set up the sector for failure.
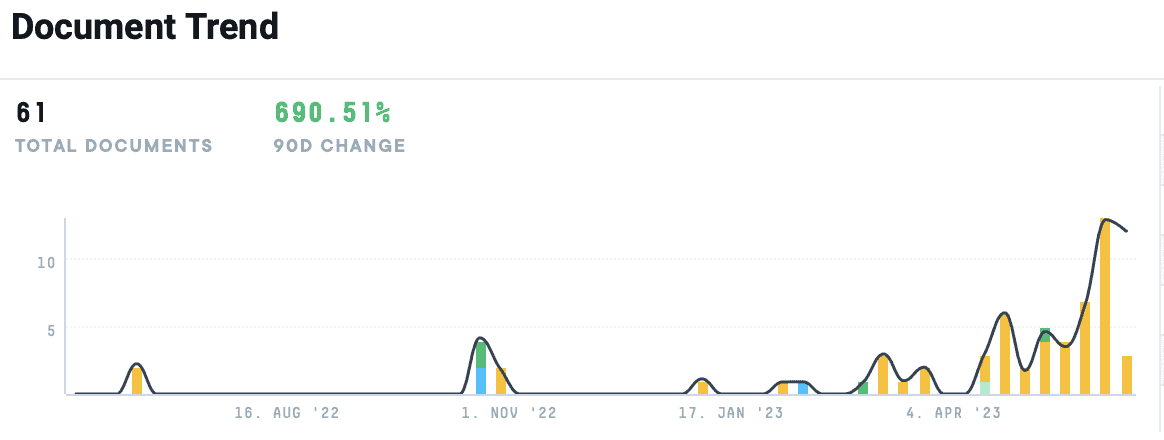
Noticing an uptick in mentions of “genAI” within the AlphaSense platform, we dove deeper into the discussion being had about this iteration of AI. From its proposed applications and the AI technology companies have already released to the shortcomings expert foresee, we’ve compiled the most crucial insights on how this groundbreaking technology is transforming the healthcare space.
GenAI in Healthcare
According to a 2023 report from Accenture, advances in large language models (LLMs)—an essential component of genAI systems—can revolutionize the healthcare industry, benefiting creativity and boosting productivity for providers and patients. Nearly all (98%) providers and (89%) executives who participated in the study believe these advancements will usher in enterprise intelligence, as 40% of all working hours could be supported or augmented by language-based AI.
In a post-pandemic world, a large percentage of medical institutions face scarce clinical resources. The biggest potential for genAI in healthcare, then, is to free overworked and underpaid employees from administrative tasks so they can work at the top of their license. “A strong digital core and investments in people will be the key to reaping the full value of generative AI in a responsible and authentic way,” Accenture writes.
However, to truly realize the full benefits of genAI, upper management will have to remodel workflows and let generative AI take over some tasks currently being accomplished by human workers. In turn, employees will have a new “9 to 5” that focuses on work that cannot be automated and, therefore, prioritizes human efficiency and effectiveness.
But the work of integrating genAI into healthcare starts with helping both clinicians and patients stay up-to-date with this technology for greater access, better experiences, and improved outcomes. Further, institutions will need to get their proprietary data ready. Foundation models for genAI need vast amounts of curated data to learn, which means organizations must take a strategic and disciplined approach to acquiring, vetting, safeguarding, and deploying data.
Fine-tuning the pre-trained LLMs with organization-specific data will allow for more accurate usage. Organizations need a modern enterprise data platform built on the cloud with a trusted set of data products. As more than half of healthcare organizations plan to use ChatGPT for learning purposes, and more than half are planning pilot cases this year, these steps will be critical in ensuring a positive outcome.
Use Cases of GenAI in Healthcare
Clinical Decision-Making
Generative AI excels at analyzing complex and diverse information sets—making it a suitable option for identifying a patient’s potential health risks. It acts as a virtual collaborator, helping healthcare providers consider a broader spectrum of variables, thus contributing to more comprehensive and personalized patient care.
Moreover, genAI doesn’t just assist with diagnosis; it also plays a crucial role in suggesting tailored treatment options. By drawing on vast databases of medical knowledge and the latest research, this technology can propose evidence-based therapies and interventions, ensuring that patients receive the most effective and individualized care.
As genAI continues to evolve, its potential to revolutionize clinical decision-making is undeniable. Primary care providers are now empowered with a valuable ally, capable of sifting through vast amounts of data, recognizing patterns, and offering valuable insights that can ultimately lead to improved patient outcomes.
Risk Prediction for Catastrophic Health Events
Generative AI models are quickly becoming indispensable in predicting catastrophic health events. Not only do they offer valuable insights for scientists studying pandemics and preventive measures, but they can also help identify new antibodies to combat infectious diseases.
For example, experts at Scripps Research and Northwestern University have created the early warning anomaly detection (EWAD) system as a way to forecast viral pandemics and, consequently, provide longer lead times to address oncoming health crises. EWAD can anticipate changes in the pattern, spread, and pathology of a virus weeks before it circulates, identifying signatures destined to become variants of concern. .
Generative AI models have also emerged as a vital resource for modeling new pandemics and developing preventive measures. Some new genAI models are currently being trained on large amounts of protein sequences to identify new antibodies that could address infectious diseases and construct outbreak responses for the future.
These advancements are revolutionizing our approach to health crises, equipping us with powerful tools for risk prediction and mitigation that enhance global healthcare preparedness.
Personalized Medication and Care
Personalized medication and care have recently taken center stage, thanks to the integration of wearable technology leveraging generative AI. MarketsandMarkets suggests that the global market for wearable healthcare devices will approach $70 billion by 2028, with annual growth in the market exceeding 11 percent per year
Wearable devices, equipped with sensors and sophisticated technology, enable the real-time and continuous collection of essential health indicators. These include heart rate variability, blood oxygen saturation levels, blood glucose levels, and more from companies like Apple, Silvertree, Abbott, and FitBit. This wealth of data not only empowers individuals to gain insights into their own health, but also offers a transformative opportunity for healthcare providers to transition from traditional reactive healthcare models to more proactive, patient-centric ones.
Wearable technology’s continuous data collection capabilities create a dynamic and comprehensive view of an individual’s health status. Generative AI p processes and makes sense of this vast amount of data by identifying trends, anomalies, and potential health risks, even before they manifest as symptoms. This predictive capability is a game-changer for healthcare, as it enables early intervention and personalized treatment plans, tailored to an individual’s unique health profile.
But the synergy between wearable technology and genAI extends beyond monitoring. It fosters a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare providers, promoting active engagement in one’s health. Patients can share their data securely with their healthcare teams, enabling a more holistic understanding of their health and fostering a proactive approach to wellness.
Improved Drug Discovery and Development
Generative AI has shown promising results in drug discovery and development (e.g., Insilico Medicine, a company that has developed a generative AI platform called GENTRL). Doctors may no longer have to rely on old-fashioned methods such as manual patient diary entries, faxed medical records, and snail-mailed findings to regulatory agencies.
The advent of generative AI is poised to revolutionize these practices. It allows for the efficient analysis of vast datasets, swiftly identifying promising candidates for clinical trials, optimizing molecular structures, and even predicting potential side effects and interactions. This unprecedented level of data processing not only expedites the discovery process but also enhances the precision and safety of drug development.
How GenAI is Transforming the Healthcare Industry
Generative AI is ushering in a profound transformation within the healthcare industry, reshaping the way care is delivered and managed on a macro scale. By harnessing the power of artificial intelligence, genAI has unlocked capabilities that were previously inconceivable, fundamentally altering the landscape.
In the past, treatments were often administered based on broad population data, with limited consideration for individual variations. GenAI, however, has made it possible to delve deep into patients’ genetic profiles, medical histories, and real-time health data. This means that healthcare can now be tailored to the unique needs and genetic makeup of each patient.
The result: a more precise, effective, and patient-centric approach to medical care that improves outcomes and reduces the occurrence of adverse effects significantly. It’s a reality that could come soon in the eyes of Americans, as more than half believe genAI will be fully embedded into healthcare/patient interactions by 2028.
Furthermore, genAI is streamlining drug discovery and development processes. Historically, the path from drug discovery to market availability has been arduous and time-consuming. By accelerating the identification of potential drug candidates, optimizing molecular structures, and even predicting side effects and drug interactions, the speed and efficiency enabled by genAI holds the promise of bringing novel and safer medications to patients.
Moreover, the healthcare industry is becoming increasingly data-driven thanks to genAI. The technology’s capacity to analyze vast datasets, detect trends, and make predictions is invaluable for proactive disease management, efficient resource allocation, and evidence-based decision-making.
These data-driven insights are reshaping public health strategies, optimizing hospital operations, and enhancing care delivery at large, ultimately leading to improved patient care and increased sustainability of healthcare systems. In this macro lens view, genAI is paving the way for a more responsive, patient-focused, and data-enhanced healthcare ecosystem that was simply beyond reach in the pre-AI era.
Industry Advancements and Growing Competition
While genAI is relatively new to the market, there’s no shortage of startups and established companies racing to be the next manufacturing leader of genAI-powered healthcare tech.
Microsoft unveiled plans last year to embed generative AI into clinical software from Epic, the biggest hospital EHR vendor in the U.S. The two companies produced the first sites integrating GPT into EHR workflows to automatically draft replies to patient messages. The companies are also bringing genAI to Epic’s hospital database, allowing laypeople to ask AI general questions instead of needing a data scientist to query specific data.
Google has joined the race by creating its large language model, called Med-PaLM 2, which is available to specific customers for use case trials. Unlike most AI algorithms, Med-PaLM was specifically trained on medical data, allowing it to sift through and make sense of massive amounts of healthcare information. While it still has room for improvement in answering queries, its performance is exceeding expectations.
Unlike Microsoft’s product, Google’s Med-PaLM won’t be for patient-facing use. Rather, hospitals could use Med-PaLM generative AI technology to analyze data to help diagnose complex diseases, fill out records, or as a concierge for patient portals.
Another use case for genAI is streamlining medical note-taking. Physicians can spend roughly six hours a day logging notes in their EHR, which leads to less time with patients and more burnout. Nuance, a documentation company owned by Microsoft, is providing a solution to this problem.
In 2023, the company announced the integration of GPT-4 into its clinical note-taking software. Last summer, Nuance allowed providers to beta test the documentation products, called DAX Express. Between 300 to 500 physicians tested the product in a private preview in mid-June, and it’s set to become available to the public in early fall of 2024.
Suki, a documentation company partnering with Google, recently launched its genAI-powered “Gen 2,” which can generate a clinical note by listening into a conversation and filling in a note automatically. Eventually, doctors will also be able to ask the AI questions and give it commands, such as graphing a patient’s A1C levels over a three-month period.
Backlash Against Generative AI
There’s no shortage of excitement around future use cases for genAI. And yet, some of its current applications have already drawn sharp backlash.
ChatGPT and GPT-4, bi-products of largely consumer-focused genAI that utilize interfaces from OpenAI, are capable of holding conversations, answering questions, and even writing low-grade high school essays. However, in The New York Times’s story focusing on the troubling conversations with Bing’s chatbot, Sydney (i.e., responses that promoted infidelity and a desire to be “alive”), fostered speculation regarding where these tools were pulling reference data from.
While tech leaders are hyping up genAI’s streamlining capabilities, conversations around automation and the role it will play in our society are running rampant, especially with regard to the healthcare sector. Ultimately, it’s a question of how much we should be relying on genAI and what the consequences of doing so are.
An AI system relies on a machine learning model to generate answers or make decisions. But how these results are produced brings into question three areas of ethical concern for society: privacy and surveillance, bias and discrimination, and the role of human judgment.
Bias then becomes another key worry with AI, especially within a healthcare setting. If an algorithm is trained on biased data, or its results are applied in biased ways, it perpetuates those biases. This leads to the question of accountability: since generative AI, and AI applications in general, are relatively new, it’s unclear if the owner, user, or developer is at fault for any negative consequences stemming from its use.
The Future of Generative AI in Healthcare
Generative AI in healthcare holds immense promise and is poised to revolutionize the industry. But while the future of this technology holds enormous potential within healthcare and outside of it, it also raises ethical and regulatory challenges, such as patient privacy and security, standardization, and ensuring equitable access to AI-powered healthcare. As these issues are addressed, genAI will usher in a more patient-centered, efficient, and data-driven field. A new era of improved health outcomes and more accessible medical services is just years, if not months, from being a reality.

Results from a Wolters Kluwer survey double down on the opportunities genAI has in healthcare: “while many Americans have concerns or even fear around genAI, 45% are starting from a position of curiosity. Over half of Americans (52%) report they would be confident in the results if they found out their own provider was using genAI to support care.” Ultimately, the success of genAI in healthcare will rely entirely on reliable technology that patients and providers can trust.
Getting the Answers You Need
In a volatile market that’s producing new developments around genAI every day, it’s challenging to decipher what technology, product, or insight could revolutionize the healthcare industry next. Cutting through the noise to find insights is nearly impossible in the age of information overload. You need a tool that does all of the heavy lifting, so you can focus on leveraging information rather than searching for it.
AlphaSense is a leading provider of market intelligence, including 10,000+ high-quality content sources from more than 1,500 leading research providers—all in a single platform. Analysts, researchers, and decision-makers in the medtech sector can access exclusive research reports only found elsewhere in disparate locations and often behind expensive paywalls. With AlphaSense, companies can conduct comprehensive research that gives them a competitive edge with smarter, more confident decision-making.
Specific types of content you’ll find on the AlphaSense platform include:
- Healthcare news, industry reports, company reports, 510(k) filings, and regulatory content from sources such as PubMed, World Health Organization, MedlinePlus, and FDA
- Over 1,500 research providers including Wall Street Insights®, a premier and exclusive equity research collection for corporate teams (healthcare included)
- Expert call transcript library that gives access to thousands of insightful interviews with healthcare professionals, customers, competitors, and industry experts
The AlphaSense platform also delivers unmatched AI search capabilities and features for analyzing qualitative and quantitative research, and can mine unstructured data for the most critical insights, including:
- Automated and customizable alerts for tracking regulatory filings, companies, industries, and potential investments
- Table export tools that support M&A workflows like target lists and due diligence
- Smart Synonyms™ technology that ensures you never miss a source important to your research
- Smart Summaries, our first generative AI feature, summarizes key insights from earnings calls for faster analysis
Don’t miss our State of Generative AI & Market Intelligence Report 2023.
Stay ahead of the rapidly evolving medtech landscape and get your competitive edge with AlphaSense. Start your free trial today.