Excitement for Generative Artificial Intelligence (genAI)—the branch of artificial intelligence that can generate images, videos, audio, text, and 3D models by studying existing data and using its findings to produce new, original data—is palpable across sectors. Already, C-Suite leaders are leveraging genAI’s ability to generate highly realistic and complex content that can mimic human thought, creativity, and speech for countless use cases.
From helping engineers develop 3-D designs to assisting data scientists in writing code and even drafting and reviewing legal documents in the legal world, there’s no shortage of evidence that genAI could be a panacea for streamlining processes and eliminating mundane, tedious work in every industry.
This is especially true of the market research and intelligence industry, where a number of companies across sectors are wielding genAI for similar purposes. But even more promising is this technology’s advancements to help companies penetrate new markets, identify untapped consumers, and aid in strategy building. This technology has led analysts and experts to forecast genAI playing an ever-increasing role in market research due to its efficiency, effectiveness, and simplicity.
In our 2023 State of Gen AI & Market Intelligence report—which surveyed 500-plus professionals across various industries including Corporate Development, Corporate Strategy, Competitive Intelligence—a vast majority (over 80%) of respondents plan to leverage genAI tools in their research this coming year.
Below, we dive into how generative AI and its abilities are being applied to current market research efforts, as well as the pros and cons of leveraging this technology.
Capabilities of Generative AI
The question on top of research professionals’ minds is simple: how can generative AI simplify and enhance the way we conduct and evaluate market research?
Unlike popular belief, genAI’s algorithm infrastructure is not only used to generate content. Rather, the capabilities used for generating output can be harnessed and applied to other processes. These contributions streamline the process of collecting and analyzing data results, which take form in real-time insights, predictive modeling, and pattern detection.
Below, we dig into what each of these AI solutions entail and how they benefit research and, ultimately, decision-making:
Predictive Modeling
Predictive modeling is a process that uses historical logs of data to forecast future outcomes. From projecting customer demand to stock prices, leadership is leveraging predictive modeling to inform buying and selling decisions, analyze competition, and improve product performance.
Pattern Detection
Pattern detection is a capability of genAI that can find patterns in data sets and decipher hidden connections between different variables . With pattern detection, researchers can explore linkages between product performance, consumer attitudes, and behaviors that would otherwise be ambiguous.
Real-time insights
Real-time insights are insights based on live data, and are used best for metrics that are constantly changing, (i.e., social media, website traffic, etc.). Real-time insights are beneficial to understanding how competitors are approaching a market, product performance, and corresponding consumer attitudes.
Applications of GenAI in Market Research
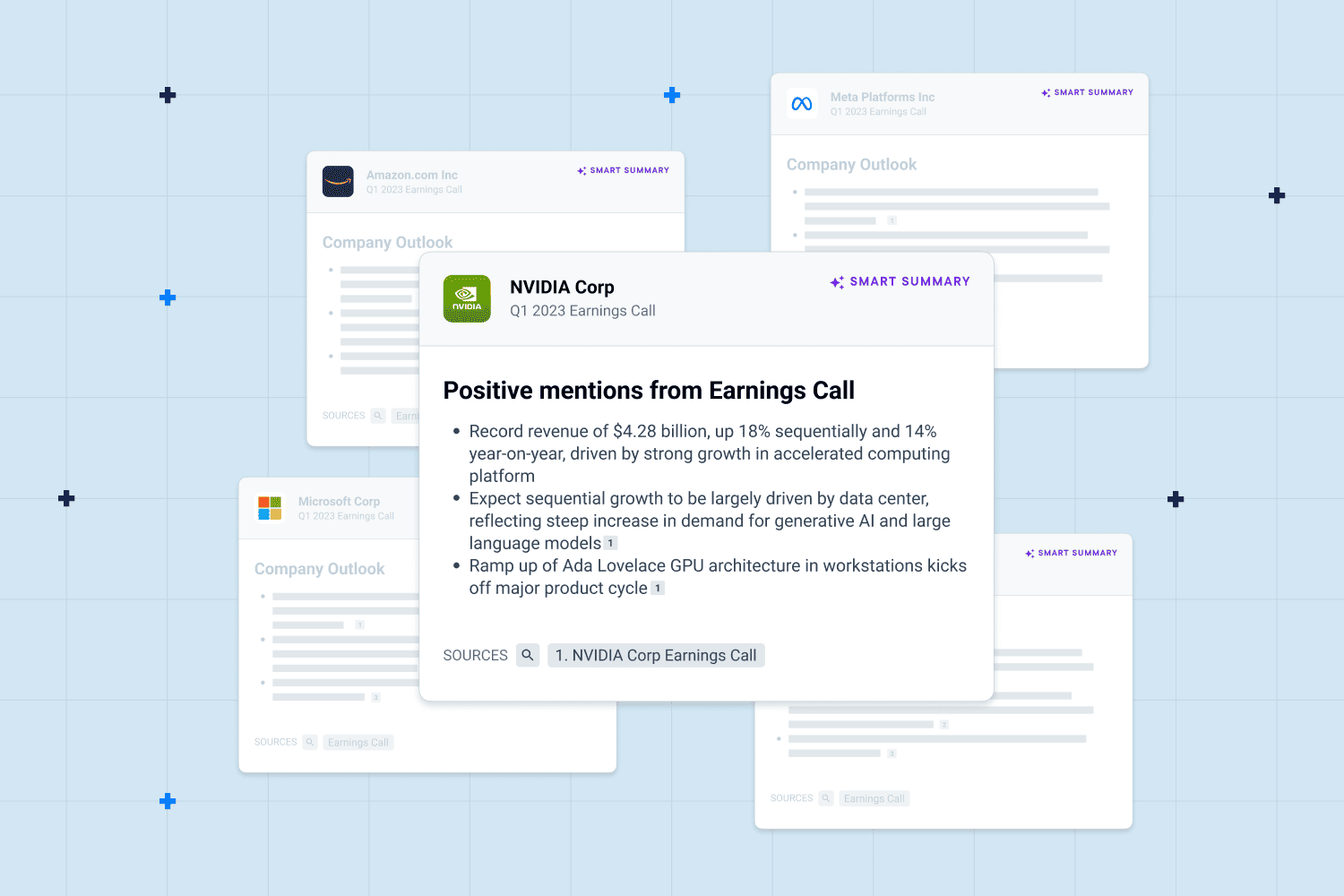
Today, many professionals find themselves manually sifting through hundreds, if not thousands, of pages of corporate communication. Generative AI offers a promising solution to this workplace obstacle—it can summarize documents in seconds with heightened accuracy. No longer do researchers have to spend hours analyzing earnings transcripts and research reports to get the information they need.
When applied in the right ways, generative AI will help market researchers find and understand new markets, monitor companies and industries, make good investments, and focus on the most profitable growth strategies. The following are some of the most promising applications of this technology:
Streamlining Earnings Analysis
Generative AI is transforming the landscape of earnings analysis in several significant ways. Firstly, it automates the extraction and processing of financial data from diverse sources, simplifying the traditionally labor-intensive task of compiling and organizing income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. This automation not only saves time but also enhances data accuracy by minimizing human errors and ensuring that earnings analysis is grounded in precise and comprehensive information.
GenAI also excels in generating summaries of investor sentiment and market movements—including everything from pre-earnings insights, highlights, lowlights, and guidance after the call. Additionally, it can quickly grasp where a company surpassed or missed expectations, and extract guidance on critical KPIs.
Furthermore, generative AI is proficient in predictive analytics, utilizing historical earnings data and external factors to forecast future earnings trends and scenarios. This empowers businesses and investors with the ability to anticipate market size and movements, adapt their investment strategies, or make informed adjustments to their business operations based on anticipated earnings outcomes.
In sum, generative AI optimizes earnings analysis by automating data processing, generating human-readable reports, and enabling predictive insights. This not only streamlines the analytical process but also enhances the accuracy and accessibility of financial information, leading to more informed investment decisions and more agile business strategies.
Gaining the Wall Street Perspective
One of the most useful qualities of genAI is that it can process vast volumes of financial and market trends in real time, identifying trends and anomalies that some human analysts might overlook.
It can analyze stock prices, trading volumes, news sentiment, and various market indicators, helping traders and financial institutions make more informed decisions. By applying predictive modeling, it can also forecast market movements and anticipate potential risks, enabling traders to optimize their strategies.
Moreover, genAI‘s natural language generation capabilities can generate in-depth financial reports, summaries of earnings calls, and market commentaries—providing context into Wall Street forecasts with quick and actionable insights..
On the other hand, for stakeholders and investors, genAI can offer a user-friendly interface to access and interpret financial data. It can provide personalized investment recommendations based on an individual’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Additionally, it can generate easy-to-understand summaries of company performance, highlighting key financial metrics, significant events, and future outlook.
This empowers stakeholders and investors to make more informed decisions about their investments and portfolios, whether they are seasoned investors or individuals with limited financial expertise. By bridging the gap between complex financial data and non-expert stakeholders, genAI democratizes access to financial insights, making it easier for a broader range of people to participate in the financial markets.
Understanding Your Position in the Market
GenAI is capable of conducting sentiment analysis and extracting valuable insights from a wide range of textual data sources, enabling it to understand and summarize what former employees, competitors, and channel partners are saying about a company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis).
For former employees, genAI can analyze comments from platforms like Glassdoor or company exit interviews to gauge sentiments regarding their experiences. By identifying recurring themes or sentiments, genAI can highlight areas where the company excels (strengths) as well as areas that need improvement (weaknesses). This information can be valuable for companies looking to enhance their employer brand and make strategic HR decisions.
In the case of competitors, genAI can scrape news articles, social media mentions, or industry reports to compile a SWOT analysis. It can pinpoint competitors’ perceived strengths and weaknesses, helping companies identify potential areas of competitive advantage.
Additionally, it can track emerging opportunities and threats within the industry, enabling businesses to pivot and adapt to changing market dynamics.
Channel partners’ feedback and discussions can also be analyzed to understand the effectiveness of the company’s partnerships and distribution strategies, shedding light on areas for improvement and collaboration. GenAI‘s ability to extract insights from this diverse textual data allows companies to make data-driven decisions and maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
Benefits of GenAI in Market Research
While being touted as a tool that simplifies tedious and time-consuming work, automating tasks, and allows teams to focus on more complex, thoughtful labor, genAI also possesses the capability to generate new market growth opportunities through machine learning.
Because genAI can easily collect data from far-reaching or remote locations, this technology can provide insights into new or neglected markets that were previously too costly to research manually. Likewise, generative AI can also identify potential target markets by analyzing existing customer data. Using this intel, genAI then generates synthetic customer data to produce a more accurate picture of what the target markets look like and how likely they are to respond to a product or service—mitigating the risk of a business venture.
More precisely, genAI is providing a bigger picture of who potential customers are and how market researchers can reach and entice them. Rather than relying on basic surveys and focus groups for understanding consumer likes and dislikes, genAI generates specific customer preferences, detailed profiles, and preferences, allowing for a more effective assessment of a target market.
In the grander scheme, genAI can also produce customized research plans based on the aforementioned data, that detail how to better reach these specific markets. And with genAI’s ability to automate the data analysis process, market researchers are given time back that was otherwise spent on the tedious analysis and structuring of a research plan.
But what most market researchers are focused on is genAI’s capability to quickly generate data—quicker than surveys, focus groups, and experiments take to produce results, making it the ideal methodology for quickly collecting accurate data.
And while there are some questions surrounding what data sets genAI pulls from to generate its results, it can ensure greater accuracy in market research data by accounting for things like changing demographics or regional preferences. Further, it prevents and removes biases from market research gatherings by using synthetically generated data and algorithms to assess the results—which are then based on collected data, without any preconceived notions about demographics or markets.
Drawbacks of GenAI in Market Research
- Scalability: While faster than conducting surveys and peer studies, generating new data can be a time-consuming process, which could lead to data that isn’t available for research teams when needed. With rushed data, there is the potential for lower levels of accuracy and, consequently, research delays.
- Accuracy: GenAI-generated data is historically reliable, but may not be as accurate as data collected through empirical research. As such, researchers should be considerate as to how they are using this data to reach target audiences. The core of an unbiased algorithm starts with the content sets it’s based on. Vetting data sources that serve as the foundation for a genAI system’s knowledge becomes critical to ensuring reliable results or decisions.
- Interpretability: The way data is transformed from raw to usable state is not entirely transparent with generative AI—where is this data being pulled from and by what means? Without this exact knowledge, market researchers will have limited insight into why their genAI data is the way it is, weakening its credibility.
- Reliability: Although genAI can write impressive texts that mimic human writing, the results can be inaccurate when based on incomplete, outdated or unverified information sources. For those wielding genAI, be cautious of the fact that most byproducts of this technology leverage unverified or unreliable sets.
Be on the Leading Edge of Generative AI
Unlike other consumer-grade generative AI tools trained on publicly available data, AlphaSense takes an entirely different approach. Our industry-leading suite of generative AI tools is purpose-built to deliver business-grade insights and leans on 10+ years of AI tech development. Our proprietary AlphaSense Large Language Model (ASLLM)—trained specifically on business and financial data—matches or beats the leading third-party LLMs over 90% of the time.
Our suite of tools currently includes:
- Smart Summaries – this feature allows you to glean instant earnings insights—reducing time spent on research during earnings season, quickly capture company outlook, and generate an expert-approved SWOT analysis straight from former competitors, partners, and employees
- Enterprise Intelligence – a first-of-its-kind offering that delivers AlphaSense’s AI-powered search and summarization capabilities to customers’ internal organizational knowledge.
- AlphaSense Assistant – a generative AI chat experience that transforms how users can extract insights from hundreds of millions of premium content sources
Looking to learn the future of generative AI? Check out our virtual event, Applying Generative AI to Market Research: Strategic Use Cases for Corporations and Investors, to learn how it can streamline your market research workflows.
Check out this case study to learn how ODDO BHF, one of the largest private banks in Germany, used AlphaSense and its genAI capabilities to streamline insights and get the competitive edge.
Start your free trial of AlphaSense today.